There are a few ways to monitor when someone makes an INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE in SQL Server. One quick and easy way is through SQL Server Audit. Below is a step-by-step way to create that audit:
Expand Security, then right-click Audits and click ‘New Audit…’
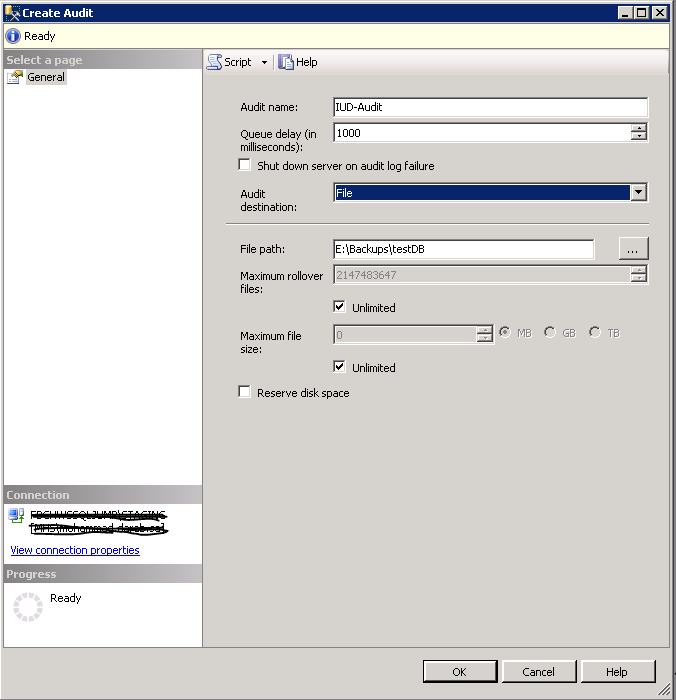
Pick how, and where, you want to save the file.
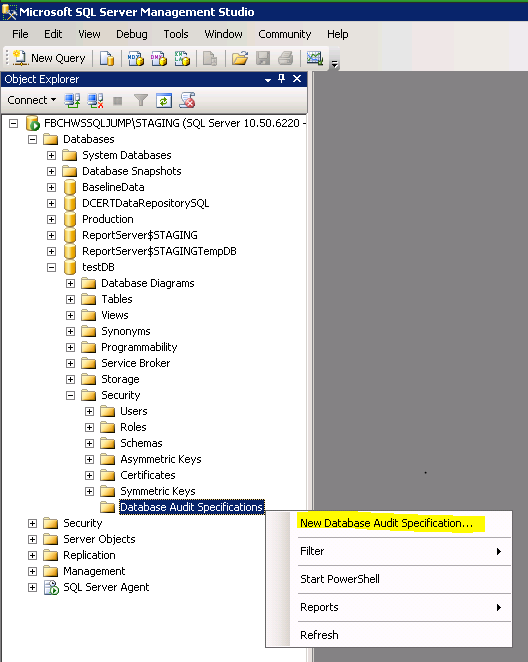
After choosing where/how to save the file, expand the database, then expand Security, right-click ‘Database Audit Specifications‘ and choose ‘New Database Audit Specification‘
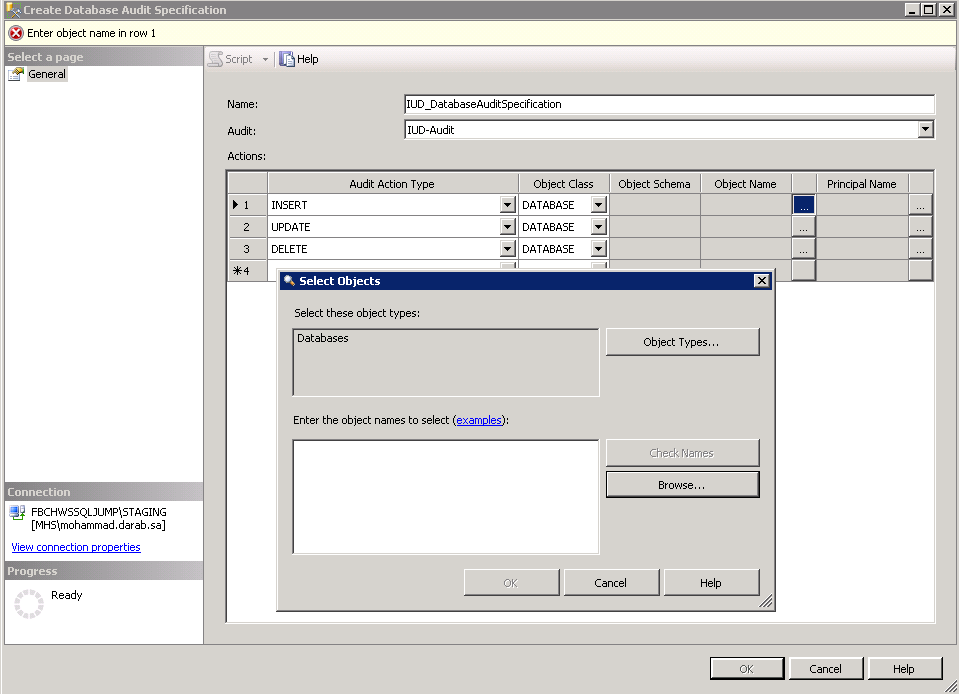
The next set of sequences all relate to what objects/permissions/roles you want to audit.
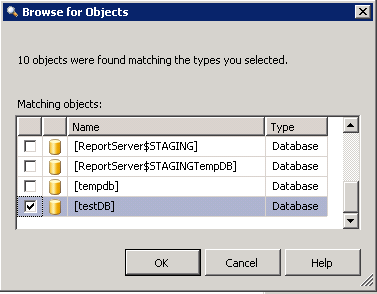
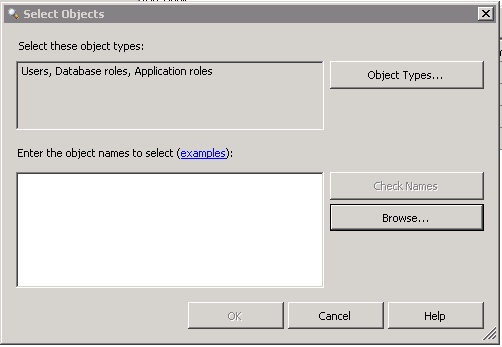
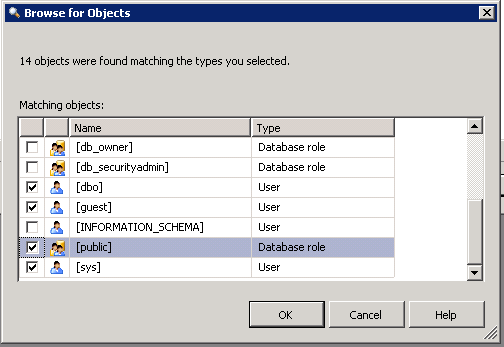
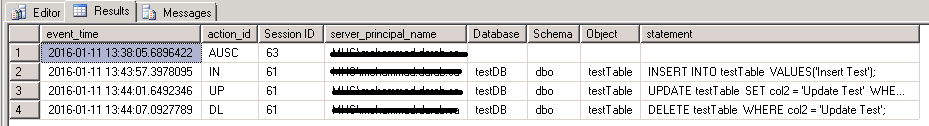
Output of fn_get_audit_file:
The code to recreate the above steps is below:
[snippet id=”52″]